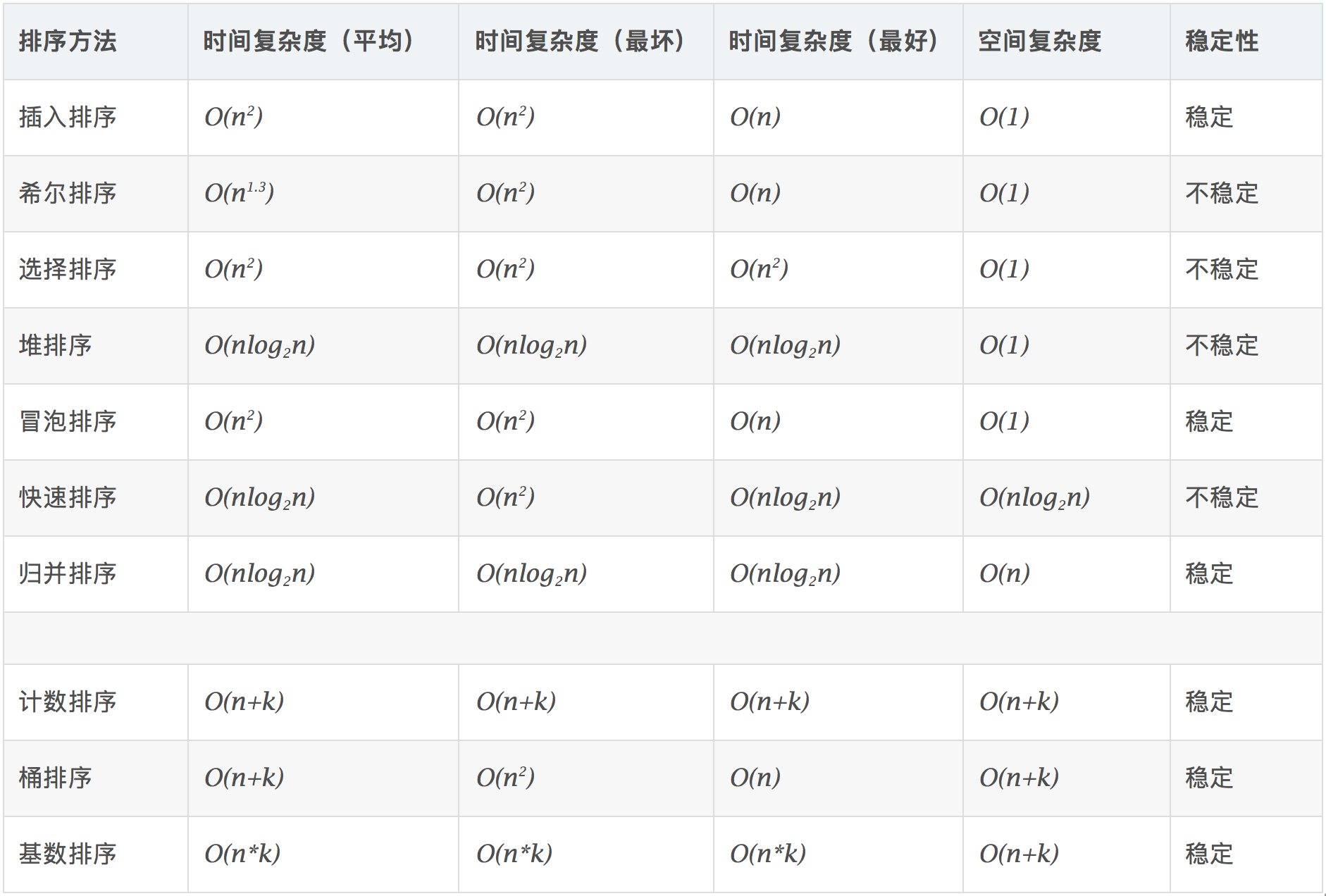
排序
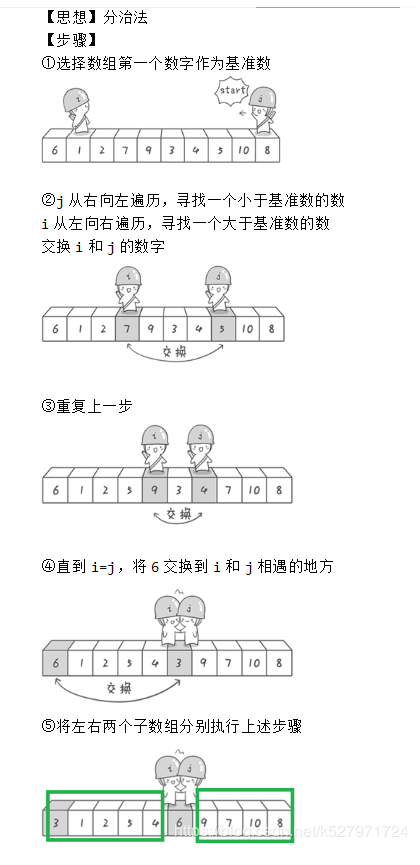
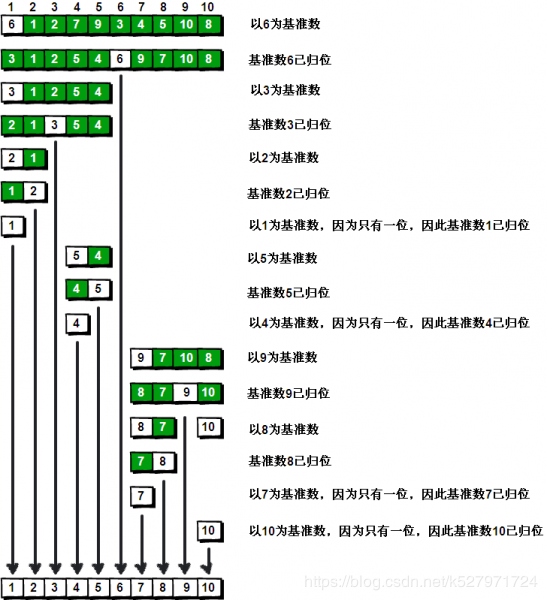
快速排序
1 | static int[] a = {6, 1, 2, 7, 9, 11, 4, 5, 10, 8}; |
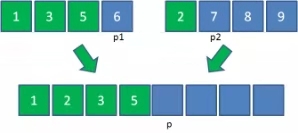
归并排序
1 | void mergeSort(int[] arr, int start, int end) { |
堆排序
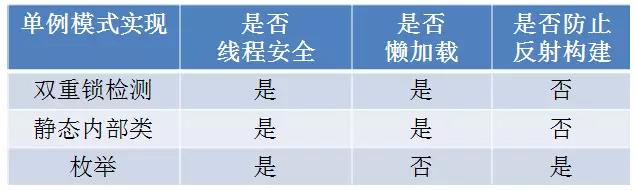
单例
双重校验锁
volatile 的一个语义禁止指令重排优化。在读取变量的时候直接从内存读取,保证所有线程看到的变量值都是相同的,
synchronized关键字锁住类
进入Synchronized 临界区以后,还要再做一次判空。因为当两个线程同时访问的时候,线程A构建完对象,线程B也已经通过了最初的判空验证,不做第二次判空的话,线程B还是会再次构建instance对象。
1 | public class Singleton { |

静态内部类
1 | public class Singleton { |
enum
1 | // JVM会组织反射获取枚举类的私有构造方法 |
链表
单链表反转
1 | Node reverse(Node head) { |
删除重复值
1 | Node deleteRepeat(Node head) { |
判断链表是否有环
1 | Node meetingNode(Node head) { |
链表中环入口节点
1 | Node nodeOfLoop(Node head) { |
判断两个链表是否相交
1 | boolean isIntersert(Node h1, Node h2) { |
二叉树
非递归遍历二叉树
栈:先入后出
1 |
|
二叉树的深度
1 | int findDeep(BiTree root) { |
层次打印二叉树
1 | void printTree(Tree root) { |
判断tree2是否为tree1子结构
1 | boolean hasSubTree(Tree root1, Tree root2) { |
数组
合并两个有序数据,结果任然有序
1 | int[] merge(int[] a, int[] b) { |
二分查找
1 | int binarySearch(int[] arr, int key) { |
矩阵
顺时针打印矩阵
剪绳子求最大乘积
动态规划
- 求问题的最优解
- 整体问题的最优解是依赖各个子问题的最优解
- 把大问题分解成若干小问题,小问题之间还有互相重叠的更小的子问题
- 从上往下分析问题,从下往上解决问题
为了避免重复求解子问题通常先计算小问题的最优解并存储下来,在以此基础求取大问题最优解。
1 | int maxCuttingSolution(int length) { |
贪婪算法
每一步都做最贪婪得选择,基于这个选择,能够得到最优解。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19/**
* 当长度>=5时,尽可能多剪长度为3得绳子,当剩下绳子长度为4时,把绳子剪成长度为2得绳子
*/
int maxCuttingSolution1(int length) {
if (length <= 2) {
return 1;
}
if (length == 3) {
return 2;
}
//尽可能剪去长度为3的绳子段
int cutThree = length / 3;
if (length - cutThree * 3 == 1) {
cutThree -= 1;
}
int cutTwo = (length - cutThree * 3) / 2;
// pow(x, y) 返回 x 的 y 次幂。
return (int) Math.pow(3, cutThree) * (int) Math.pow(2, cutTwo);
}